Shipbuilding steel plate refers to the carbon and alloy steel plate used in offshore and marine contructions, common grades are A, B, D, E, AH32/36/40, DH32/36/40, and EH32/36/40 which ranged from different strength. The plates usually used to manufacture ship hulls, bulkheads, upper decks and hatch covers for tankers, bulk carriers, container ships and LNG carriers.
AH36, DH36, EH36 Steel – Common Use High Strength Steel in Offshore & Marine
For the high strength shipbuilding plates like AH36, DH36, EH36 steel plate, they have been widely used in high stress areas of ships, comparing with general strength steel, they are offering the same strength with the smaller thickness.
Materials
Shipbuilding steel material in carbon and alloy steel, compatible with high strength, low temperature and high heat input soldering.
Shipbuiding Standards from Different Countries
Shipbuilding steel plates are produced under the approval of production methods of classification societies in different countries refers to offshore and marine steels.
- ABS (American Bureau of Shipping)
- BV (Bureau Veritas)
- CCS (China Classification Society)
- DNV (Det Norske Veritas)
- GL (Germanischer Lloyd)
- HR (Hellenic Register of Shipping)
- KR (Korean Register of Shipping)
- LR (Lloyd’s Register of Shipping)
- NK (Nippon Kaiji Kyokai)
- RINA (Registro Italiano Navale)
- RS (India Register of Shipping)
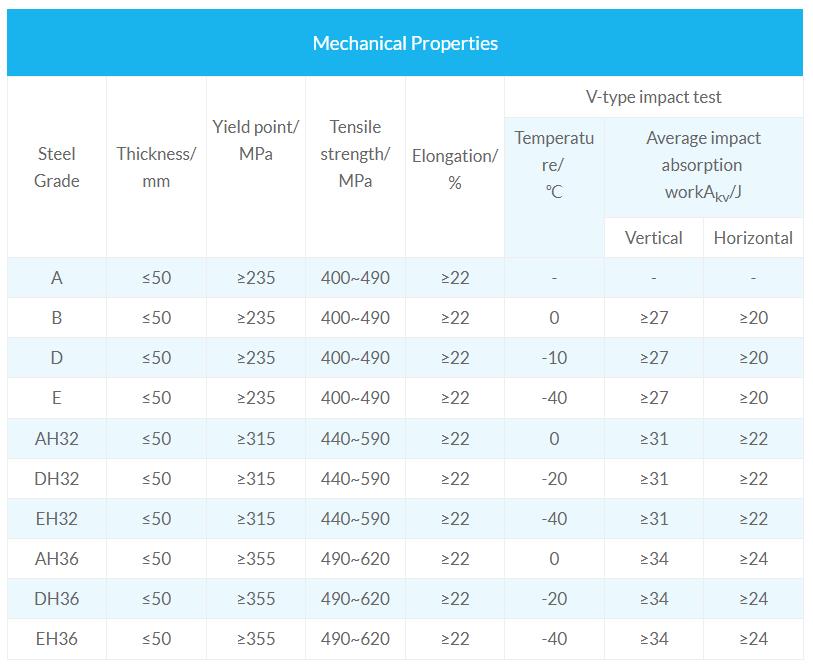
Grades: A, B, D, E, AH32/36/40, DH32/36/40, EH32/36/40
According to its yield strength, shipbuilding plate of can be divided into below grades:
- Grade A steel is the impact force subjected to normal temperature (20 ° C).
- Grade B steel impact force at 0 °C.
- Grade D steel impact force at -20 °C.
- Grade E steel impact force at -40 °C.
- High-strength shipbuilding steel plate can be further divided into: AH32, DH32, EH32; AH36, DH36, EH36 and AH40, DH40, EH40.1. The general grades A, B, D, and E are distinguished according to the impact temperature of the steel. The impact values of all grades of steel are the same.2. High-intensity hull structure steel preheating requirements: For all AH, DH, EH plate thickness greater than 30mm angle, butt joints, shall be preheating to 120 ~ 150 °C before welding.3. For thickness of the plate ≤ 30mm, the ambient temperature is below 5 ° C, preheated to 75 ° C; Ambient temperature below 0 ° C, preheated to 75 ~ 100 ° C.
Dimensions Range
Thickness Range: 5 mm -150 mm
Width Range: 1500 mm – 3900 mm
Length Range: 6 m, 12 m, coils
Surface Treatment
With anti-rust painting.
Chemical and Mechanical Requirements
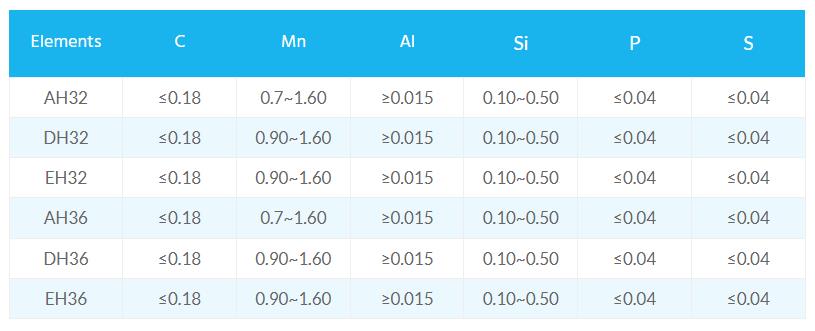
C (carbon) is an indispensable strengthening element in steel, but the increase in C content reduces the low-temperature impact toughness of steel and deteriorates the weldability of steel. Therefore, it is necessary to control the C content in the steel.
According to the experience of producing aluminsum-containing steel, in order to ensure the aluminum content in the steel and the fluidity of the molten steel, the method of pre-deoxidation is strictly to control the carbon content of the end point and the alloying of the large-pack alloy to control the oxidation of the molten steel. The way of adding aluminum.
In order to ensure good low temperature impact toughness of the steel grade, the rolling of the 355MPa class ship plate adopts a strict type II controlled rolling process.
Processing for Different Grades
Grade A and B
The general strength of grade A and B shipbuilding steel plates can meet the requirements of process and mechanical properties through ordinary rolling, so the production process is relatively simple.
Grade D, E (DH32, DH36, EH 32, EH 36)
Grade D and E series (inlcuding AH32/36, DH32, DH36, EH32, EH36) shipbuilding steel plates require good low temperature toughness and good welding performance. The production high-strength shipbuilding steel plate needs to be normalized by means of controlled rolling and controlled cooling or heat treatment processes with more complete equipment. At the same time, the internal steel purity of the supplied billets is required to be high, especially the content of S, P, N, 0 and H in the steel should be strictly controlled.
Alloy Elements Added to Improve Toughness
In order to ensure the performance of high-strength ship plates, micro-alloying technology is adopted. By adding Nb, V, Ti and other alloying elements to the steel, combined with the controlled rolling process, the grain is refined and the toughness is improved.
Direction of Development for Shipbuilding Plate
High strength, high specification, with the ship’s large-scale and safety, and changes in coating specifications, the demand for ordinary A-class panels is gradually reduced, and the demand for high-strength panels is increasing, which is concentrated in large ships of 5m wide. Plate, 200-300mm thickness special thick ship board.


